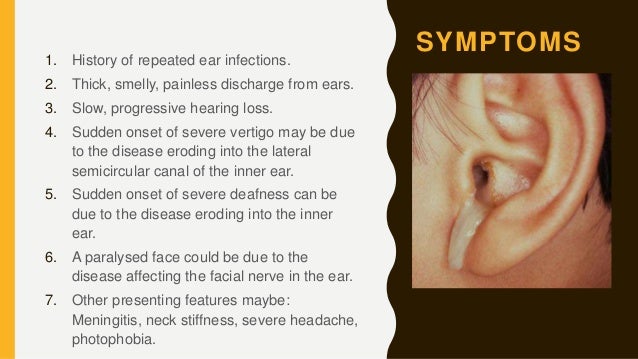
If untreated a cholesteatoma can eat into the three small bones located in the middle ear the malleus incus and stapes collectively called ossicles which can result in nerve deterioration.
Cholesteatoma of attic definition.
You can get a cholesteatoma if the eardrum is damaged through an injury or infection or after any kind of ear surgery.
It starts out as a build up of skin cells and earwax that then becomes a lump.
A cholesteatoma is a skin growth in your middle ear behind your eardrum.
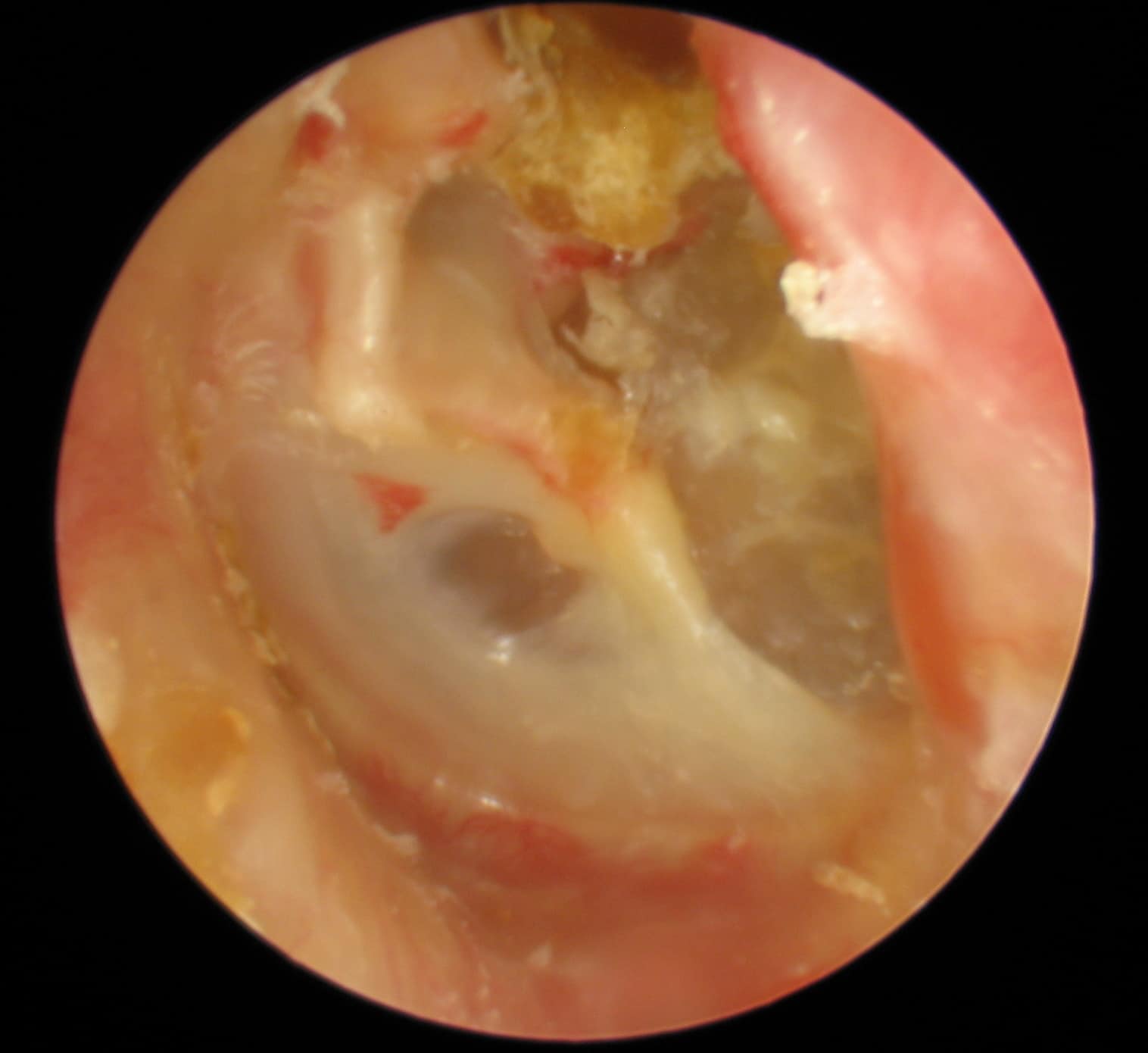
No landmarks are visible which typically is the case with advanced cholesteatomas.
The attic is just above the eardrum.
Eustachian tube theory.
With these findings recurrent cholesteatoma can be detected with 100 specificity.
Ct is required for preoperative planning reconstruction of ossicles if.
It often develops as a cyst that sheds layers of old skin and may.
As skin cells gather the cholesteatoma grows.
Cholesteatoma ko le ste ah to mah a cystlike mass with a lining of stratified squamous epithelium filled with desquamating debris frequently including cholesterol.
Wikipedia lexilogos oxford cambridge chambers harrap wordreference collins lexibase dictionaries merriam webster.
Diagnosis is clinical based on histor.
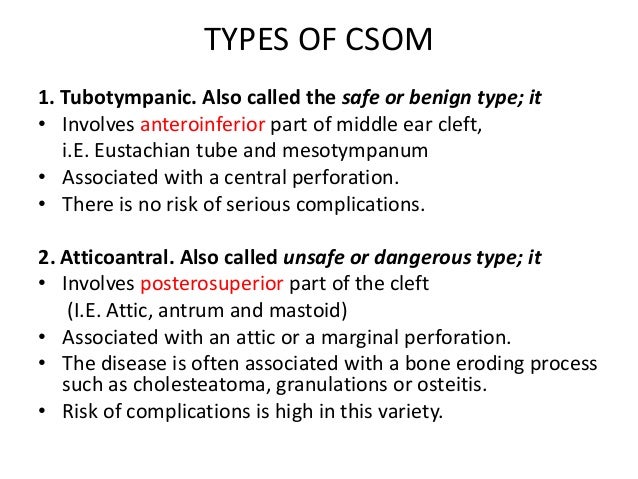
This is the most common and widely considered as the main reason for cholesteatoma.
Cholesteatoma is an accumulation of squamous epithelium and keratin debris that usually involves the middle ear and mastoid.
An ear cholesteatoma is a non cancerous growth that can cause serious complications.
Search attic cholesteatoma and thousands of other words in english cobuild dictionary from reverso.
Often presents with a malodorous ear discharge with associated hearing loss.
A cholesteatoma can develop if part of the eardrum collapses.
Cholesteatomas are most common in the middle ear and mastoid region secondary to trauma or infection that undergoes faulty healing so that epithelium invaginates.
Dead skin cells are normally passed out of the ear but if the eardrum collapses it may create a pocket where the dead skin cells can collect.
This is a typical primary acquired cholesteatoma in its earliest stages.
Invagination of the tympanic membrane of the attic to form retraction pockets to be filled with desquamated epithelium and keratin to form cholesteatoma.
A ct scan should be added in those cases where a cholesteatoma is detected with mri.
A cholesteatoma is an abnormal noncancerous skin growth that can develop in the middle section of your ear behind the eardrum.
If the cholesteatoma has been dry the cholesteatoma may present the appearance of wax over the attic.
Cholesteatomas down to a size of 2 mm can be detected with this technique on a 1 5 t mri machine.